How to Choose the Right EV Charger for Your Car: A Complete Guide for Owners
Step 1: Understand the Different EV Charger Types
The first thing you need to understand is that there are several types of EV chargers, each offering different charging speeds and compatibility. The key to selecting the right charger starts with knowing what your vehicle needs. Here are the most common types of EV chargers:
1. **Level 1 Charging (120V AC)**
Level 1 chargers are the slowest type of charging station. They use a standard 120-volt household outlet, similar to the type of outlets found in most homes. This makes Level 1 chargers highly accessible but also the least efficient for quick charging.
- **Charging speed**: Level 1 chargers typically add around 3 to 5 miles of range per hour of charging, which makes them best suited for overnight charging or for use in emergencies.
- **Use case**: Level 1 chargers are ideal for drivers who have the luxury of charging overnight and don't need to quickly replenish their battery.
2. **Level 2 Charging (240V AC)**
Level 2 chargers are commonly found in both home installations and public charging stations. They require a 240-volt outlet, which is similar to the kind of outlet used by electric dryers or ovens. Level 2 chargers are significantly faster than Level 1 and can charge a vehicle in a matter of hours.
- **Charging speed**: Level 2 chargers add 10 to 60 miles of range per hour of charging, depending on the car and the charger’s power rating.
- **Use case**: Perfect for home installations, workplaces, and public charging stations, Level 2 chargers are generally the most widely used type for most electric vehicle owners.
3. **DC Fast Charging (Level 3)**
DC Fast Charging, often referred to as Level 3 charging, is the fastest charging option available. Unlike Level 1 and Level 2 chargers that use alternating current (AC), Level 3 chargers deliver direct current (DC) directly to the battery. This allows for much faster charging.
- **Charging speed**: DC fast chargers can charge an EV up to 80% in as little as 30 minutes, making them ideal for long trips and quick stops on the road.
- **Use case**: Typically found along highways and at high-speed charging stations, DC fast chargers are often used by drivers on long trips who need to quickly recharge their EVs.
4. **Tesla Supercharger**
The Tesla Supercharger network is a proprietary network of high-speed chargers exclusive to Tesla vehicles. These chargers are optimized for Tesla’s battery technology, offering lightning-fast charging speeds.
- **Charging speed**: Tesla Superchargers can add up to 200 miles of range in just 15 minutes, depending on the model.
- **Use case**: If you own a Tesla, the Supercharger network is your go-to option for long trips. However, Tesla owners can also use non-Tesla chargers with an adapter, although this is not as fast or as seamless as using Tesla's dedicated network.

Step 2: Check Your EV’s Charging Port Type
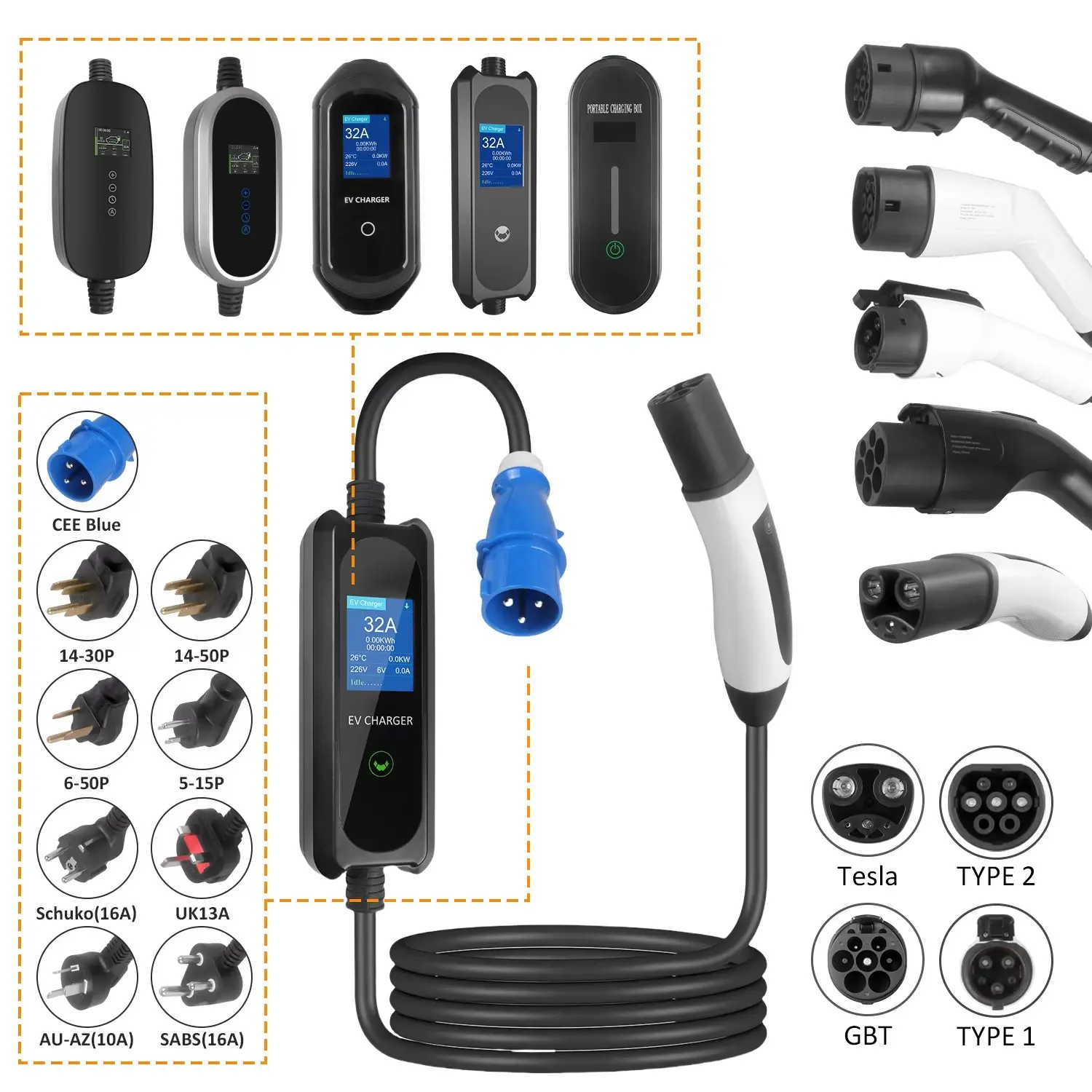
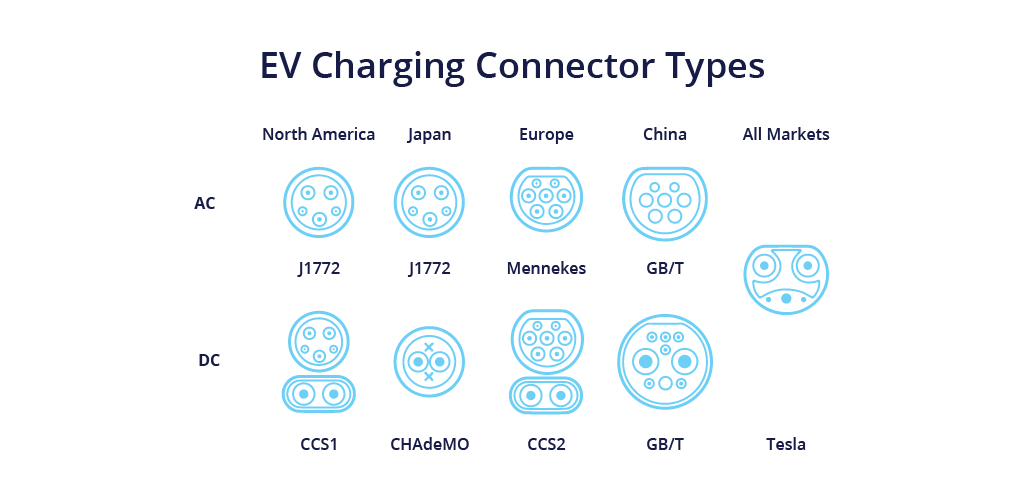
Not all EVs have the same charging port, and that’s where the real complexity lies when choosing the right charger. Each type of charger uses a different type of plug or connector, and your vehicle will only be able to charge with the compatible plug type.
To determine which charger to use, you’ll need to know which type of charging port your EV uses. Below are the most common types of connectors:
1. **CHAdeMO Connector**
The CHAdeMO connector is primarily used by Japanese manufacturers like Nissan and Mitsubishi. If your vehicle is a Nissan Leaf or another EV model that uses this standard, you will need a CHAdeMO-compatible charging station to fast charge your car.
- **Common vehicles using CHAdeMO**: Nissan Leaf, Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV, Kia Soul EV (older models).
- **Charging speed**: CHAdeMO chargers can charge your car at a rate of up to 50 kW.
2. **CCS (Combined Charging System) Connector**
The CCS connector is the most widely used charging standard in Europe and North America, and it's gaining popularity worldwide. It’s used by a variety of automakers, including Ford, BMW, Audi, and Volkswagen.
- **Common vehicles using CCS**: BMW i3, Chevrolet Bolt, Audi e-Tron, Volkswagen ID.4.
- **Charging speed**: CCS chargers can provide fast charging speeds up to 350 kW, depending on the station.
3. **Type 2 Connector**
The Type 2 connector is the most common charging port in Europe and is often used for Level 2 charging stations. It’s the standard for AC charging in most European EVs.
- **Common vehicles using Type 2**: Most European electric vehicles like the Renault Zoe, BMW i3, and Volkswagen ID.3 use the Type 2 connector for Level 2 charging.
- **Charging speed**: Type 2 chargers can support charging speeds of up to 22 kW.
4. **Tesla Proprietary Connector**
Tesla uses its own proprietary connector for charging. While Teslas can use Level 1 and Level 2 chargers (with an adapter), Tesla vehicles are optimized to use the Tesla Supercharger network for DC fast charging.
- **Charging speed**: Tesla Superchargers are capable of charging a Tesla vehicle at speeds up to 250 kW, significantly reducing the time needed for long road trips.
- **Use case**: Exclusively for Tesla vehicles, although non-Tesla EV owners can use Tesla charging stations with an adapter in some locations.
Step 3: Consider Your Charging Needs
Once you know what type of charging port your vehicle has, you can assess your charging needs to determine the best charger for you.
- **Home charging**: For everyday use, a Level 2 charger is the most practical and convenient. If your home already has a 240V outlet, you can have a Level 2 charger installed for faster and more efficient charging.
- **Public charging**: Many public charging stations offer a mix of Level 2 and DC fast chargers, but it’s important to use an app like PlugShare or ChargePoint to find stations that are compatible with your vehicle’s charging port.
- **Long trips**: For long-distance travel, fast chargers like DC Fast Charging or Tesla Superchargers are your best bet. These chargers provide high-speed charging that can get you back on the road in no time.
Step 4: Check the Charging Network Availability
If you’re planning to use public charging stations regularly, it’s essential to consider the availability and coverage of the charging network. Some networks are more widespread than others, and certain automakers may have partnerships with specific networks.
- **Tesla Superchargers**: Tesla offers an exclusive network of Superchargers that are only accessible by Tesla owners. However, the company is increasingly opening up some of its chargers to non-Tesla EVs in certain regions.
- **Public charging stations**: Many public charging networks, such as ChargePoint, Blink, and Electrify America, support a wide range of vehicles and offer various charging speeds. Check the compatibility of your EV’s charging port before relying on these stations for long trips.

Step 5: Stay Up-to-Date with New Charging Technologies
As the EV market continues to evolve, new charging standards and technologies are constantly being developed. For example, wireless charging technology is in the works, which could eliminate the need for plugs altogether. Keep an eye on industry developments, as this could change the way you charge your vehicle in the future.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right EV Charger for Your Vehicle
The key to choosing the right EV charger starts with understanding the type of charging port your vehicle uses. Once you know that, you can choose the most appropriate charger based on your needs, whether it's for home charging, public charging stations, or fast charging during long trips.
By familiarizing yourself with the different charging standards—Level 1, Level 2, DC fast charging, and Tesla’s proprietary Supercharger—you can ensure that you’re prepared to charge your electric vehicle efficiently and conveniently. Moreover, understanding your vehicle's charging port type will help you avoid confusion when using public chargers or setting up home charging stations.
In the rapidly evolving world of electric vehicles, knowledge is power—so make sure you understand your EV’s charging requirements and stay up-to-date with the latest charging options available. This will help you maximize your EV ownership experience, reduce downtime, and enjoy the benefits of driving green.